Cobot Market to Grow as Adoption in Various Industries Rises
Robot deployments continue to grow as various industries look to automate a number of processes to improve productivity and efficiency. Collaborative robots (cobots) account for a large portion of the robotics market as they can be used for a range of tasks alongside human workers.
New data from the Association for Advancing Automation (A3) shows that cobots accounted for 11.6% of all robots ordered and 6.8% of total revenue during the first quarter (Q1) of 2025. Alex Shikany, Executive Vice President at A3, stated in the association’s North American robot orders report that cobots are one of the fastest-growing areas of robotics adoption.
Research firm IDTechEx is also seeing increased uptake of cobots; it is forecasting the global market will achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.8% over the next 20 years. In its report "Collaborative Robots 2025-2045: Technologies, Players, and Markets," IDTechEx noted use of cobots will continue to grow in the coming years due to the many benefits they offer, including their ability to be used alongside human workers.
Increasing adoption in various industries and the several benefits provided are expected to help drive future growth for the cobot market.
Why This Matters
Robotics is a market in which many hydraulic, pneumatic and other motion control technologies are utilized. End-of-arm tooling — the equipment at the end of a robot arm that interacts with objects to complete a task — in particular commonly uses pneumatics. Therefore, it is beneficial for fluid power and other motion control companies to have an understanding of how the cobot and overall robotics market is projected to perform as it can help determine where these suppliers may want to focus their own development and other efforts.
Industries Driving Cobot Market Growth
According to IDTechEx, cobots can be used in a number of industries including automotive, food & beverage, semiconductors, packaging and machine tending. It cites the low cost, small footprint and ease of programming — all of which is especially beneficial for small- to medium-sized businesses — as key factors for their use in these and other industries.
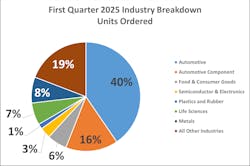
A3’s North American robot orders report shows that during Q1 2025, cobot demand was strongest in the following industries:
- Life Sciences/Pharma/Biomed: 127 units ($7.1M)
- Food & Consumer Goods: 114 units ($4.5M)
- All Other Industries: 419 units ($13.5M)
Per A3, cobots accounted for over 20% of total demand in each of these segments, helping demonstrate their increasing implementation.
Both A3 and IDTechEx noted in their reports the automotive sector being a large demand driver for the overall robotics market, including cobots (see sidebar at the end of this article for more insights from A3's Q1 robot orders report).
IDTechEx said in its report that the automotive industry is where the majority of cobot adoption is taking place as these robots can be used for several tasks such as car assembly (e.g., welding, assembling dashboards, etc.), surface polishing, and screwing. The ease of programming and flexibility offered by cobots makes it easier for automakers to retrofit or reconfigure their production lines when necessary.
The adaptability of cobots to new production line configurations is an increasingly important aspect due to the growth of electric vehicles (EV) in this sector the research firm noted. Automotive manufacturers often need to modify production lines for the new EV models they develop. Therefore, the plug-and-play nature of cobots as well as their ability to easily be reprogrammed make them a good fit for manufacturers in the EV space.
The food & beverage market is another high potential area IDTechEx sees for cobots. In this sector they are often used for high-mix low-volume production such as picking and sorting the research firm noted. Limited budgets, technical capabilities and a lack of understanding of the payback time are challenges it sees in this market segment, but in general IDTechEx believes there is long-term potential for cobots in the food & beverage industry.
Emerging market opportunities IDTechEx sees for cobots are in semiconductors and battery recycling. Both industries have grown in recent years and could benefit from the use of cobots and other automation technologies. However, use cases in both are so far limited and there are some technological challenges.
For semiconductors, IDTechEx said there are still hurdles to overcome related to ensuring cobots meet stringent cleanliness requirements. Performing the ultra-precise tasks required for semiconductor manufacturing remains a challenge for many cobots currently in the market as well.
Rising use of electric vehicles means there is also an increased need to recycle EV batteries once they reach their end of life. This is a market that is still being developed but is expected to grow in the coming years. IDTechEx said use of cobots has so far been limited in this sector and there are still many challenges the market is working through such as standardizing the battery disassembly process. But it is a segment cobot developers and their suppliers should monitor due to the potential opportunities it presents as its various challenges are overcome.
The Benefits of Collaborative Robots are Helping Drive Market Uptake
In its report, IDTechEx defines cobots as a type of lightweight and slow-moving robot which is designed to work next to human operators. Traditional industrial robots typically need to be completely isolated because of their operational speeds and force as well as the potential safety risks they pose, the research firm explained.
Cobots, on the other hand, operate at lower speeds and forces which helps make it safer for them to be used near humans without use of a physical fence. A number of safety features such as force-limiting joints and proximity sensors are also embedded into cobots to ensure safe operation near humans.
The research firm noted that as reshoring efforts occur around the globe and companies look to bring human workers back into many of their factories where possible, there is likely to be an uptick in cobot deployments because they can more easily work alongside human personnel.
Besides their ability to work in tandem with humans, cobots offer a number of other benefits as well which are helping drive their market uptake.
Reduced Downtime for Maintenance
Among the many benefits of utilizing collaborative robots is how much easier they are to work with or around when a maintenance issue occurs.
Per IDTechEx, if a traditional robot malfunctions it could cause an entire production line to be shut down so maintenance personnel can safely access them. Cobots, however, require only part of the production line to be shut down for servicing, and are generally safer to work around, which can help reduce downtime and costs.
Use of Advanced Sensor Technology
Cobots are equipped with various sensors which play an important role in ensuring they can be safely used around humans. Advanced force and torque sensors are the most commonly used, said IDTechEx, with six-axis torque sensors typically embedded at each joint of the robot. This enables real-time feedback control and the ability to detect external forces with a high degree of precision — usually within a range of 0.1-0.5 Nm.
With this level of sensitivity, a cobot will stop the moment there is unexpected resistance such as a human hand or other obstacle. In addition to safety, this capability also aids the robot’s use for fine manipulation tasks such as surface polishing or delicate part insertion said the research firm. Through their use of advanced sensor technologies, IDTechEx said cobots are able to maintain consistent pressure (e.g., 5-15 N) across surfaces, which can greatly improve finish quality and consistency.
Also noted in IDTechEx’s research report is the fact there are emerging sensor technologies coming into the market such as tactile and proximity options that could further improve the precision and safety features of cobots, and thus aid future market adoption.
Machine Vision and AI Integration
Continued developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine vision are aiding the capabilities of cobots as well. Vision systems are commonly used with cobots for object detection, part orientation and quality control. Integration of AI into these systems helps enhance machine vision for improved identification of defects and adaptation to varying part geometries.
IDTechEx offered the example of cobots that are used in car dashboard assembly. By utilizing machine vision, they can dynamically locate and align with pre-installed components to provide increased accuracy without relying on fixed jigs.
The research firm also noted further advancements in AI could help bring additional functionalities to cobots as well as the ability to make remote software updates.
Ease of Programming
Per IDTechEx, cobots are easier to program than traditional robots because they feature intuitive programming interfaces. Traditional robots, on the other hand, tend to require proprietary scripting languages and specialist programmers.
The research firm explained that the programming interfaces for many cobots utilize graphical user interfaces (GUI) with drag-and-drop logic; most of the technical details are built in and users simply need to pick the functions they want to use.
Some cobots also support manual "lead-through teaching," it said where an operator physically guides the arm through desired motions. This can cut deployment time by over 70% stated IDTechEx which again can ease set up or any reprogramming that may be required.
Support of Modular End-Effectors
Collaborative robots use a range of end-effectors, also called end-of-arm tooling (EOAT), to interact with objects, such as grippers, suction cups or welding torches. EOAT can be quickly swapped when needed, enabling a single cobot to be used for multiple tasks. This helps to maximize their usefulness and improve productivity for users.
IDTechEx anticipates some growth for the EOAT market in conjunction with increasing adoption of cobots, although it noted that because different cobots can share these devices their market saturation is likely to occur sooner.
In general, the cobot market looks to be on a positive trajectory due to the many benefits offered by these robots which is helping increase their uptake in a range of industries. Continued growth of the cobot market will likely benefit the overall robot market in the coming years as well as companies look to implement more automation to help overcome labor challenges and increase the efficiency of their operations.
About the Author
Sara Jensen
Executive Editor, Power & Motion
Sara Jensen is executive editor of Power & Motion, directing expanded coverage into the modern fluid power space, as well as mechatronic and smart technologies. She has over 15 years of publishing experience. Prior to Power & Motion she spent 11 years with a trade publication for engineers of heavy-duty equipment, the last 3 of which were as the editor and brand lead. Over the course of her time in the B2B industry, Sara has gained an extensive knowledge of various heavy-duty equipment industries — including construction, agriculture, mining and on-road trucks —along with the systems and market trends which impact them such as fluid power and electronic motion control technologies.
You can follow Sara and Power & Motion via the following social media handles:
X (formerly Twitter): @TechnlgyEditor and @PowerMotionTech
LinkedIn: @SaraJensen and @Power&Motion
Facebook: @PowerMotionTech

Leaders relevant to this article: