Zn-Ni fights corrosion better than chrome on hydraulic components
Zn-Ni fights corrosion better than chrome on hydraulic components Appeared in print as "Chrome is out, zinc-nickel is in"
The European Union’s End-of-Life Vehicles Directive No. 2000/53/EG prohibits the use of hexavalent chromium in materials and components used in vehicle manufacture for the last three years. this spelled the end to the use of hexavalent chromium (cr-vi)-containing coatings previously used for corrosion resistance in passenger cars and vehicles weighing up to 3.5 tons. and many experts feel it’s only a matter of time before the directive encompasses off-highway equipment as well. so considering the extensive use of hydraulic fittings used in most mobile equipment, the exit of cr-vi will affect suppliers, vehicle manufacturers, and recycling.
After years of electroplating Cr-VI onto components for corrosion resistance, industry is demanding replacement materials in recognition of the need to reduce, and eventually avoid, releasing quantities of hazardous materials into the environment.
Since early 2007, Voss Fluid GmbH, Wipperfürth, Germany, has been replacing its previously used yellow chromated surface finish with a proprietary Cr-VI-free zinc-nickel material that now encompasses its entire tube fittings line, flange connections, and hydraulic valves and accessories. The new finish exceeds market requirements and offers high environmental compatibility and a clean appearance.
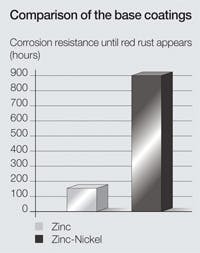
Long-term reliability
Other companies introduced a zinc thick-film passivation containing nano particles, but Voss focused research and development using a yellow chromated (A3C) surface. In salt spray tests, the surface coated with A3C is exposed to a salt mist that makes its corrosion resistance effectiveness visible. Even when suffering surface damage from handling and installation, the A3C coating exhibits high corrosion resistance against the formation of white rust and subsequent red rust.
In Voss Fluid’s R&D department’s opinion, surfaces of zinc with passivation and sealing layers offered inadequate protection and did not offer an equivalent self-healing effect. In spite of having the same zinc base coating as used for the yellow chromation and additional passivation and sealing layers, the degree of corrosion resistance drops rapidly after the sealing layer has been damaged. The R&D team sought greater corrosion resistance than that offered by a zinc base coating only — which is essential for tube joints.
The Voss zinc-nickel coating has a nickel content of 12-16% and a total thickness of 6-15 μm, which are key to attaining high corrosion resistance. In accordance with DIN 50021-SS, red rust occurs only after over 720 hr. The Voss zinc-nickel finish complies with the requirements of both the Endof- Life Vehicles Directive and the EU Directive 2002/95/EG, also known as Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive.
In addition to offering higher corrosion resistance than zinc only, the Voss zinc-nickel base coating does not form any pronounced white rust like zinc does. Instead, it produces only a light gray haze — any efflorescence with zinc oxide is prevented. These benefits have made zinc-nickel a well-proven base coating for European vehicle manufacturers.
Hydraulic system compatibility
Coefficients of friction, which are important during assembly, remain unchanged with the Voss zincnickel coating. Therefore, fittings can be tightened to the same torque levels as those in the past, and the information in existing handbooks remains valid. Furthermore, the metallic gray surface finish usually can be covered with commercially available paints. However, the precise performance of specific paints should undergo experimental testing.
The Voss zinc-nickel coating is compatible with all types of hydraulic oil.
For more information, call Mike Purdy at (330) 668-1504 or visit www.voss-zink-nickel.com.